Peripheral neuropathy is any form of weakness or damage to the peripheral nerves of the human body. Our nervous system is divided into 2 –
1.Central Nervous system (CNS) 2.Peripheral nervous system (PNS)
The CNS is the brain and the spinal cord The PNS is the set of peripheral nerves that originate from the CNS. These spread forth and cover the upper and lower limbs and rest of the body.
What are the different peripheral nerves ?
Peripheral nerves are of the following different types –
1.Sensory nerves. 2.Motor nerves. 3.Autonomic nerves.
Sensory nerves : are smaller nerves that are mainly needed for sensations – touch, pain, sensation of heat, cold etc.
Motor nerves – These are larger nerves that mainly provide power. They are necessary for all our movements and activity.
Autonomic nerves – These are mainly responsible for correct functioning of our internal organs, body temperature regulation sweating etc.
What happens in peripheral neuropathy ?
How does diabetes cause peripheral neuropathy ?
There are multiple reasons and ways in which diabetes can cause peripheral neuropathy. In simple terms, these are –
Micro blood vessels damage : Diabetes causes the damage of micro blood vessels that directly supply the peripheral nerves. This causes loss of nutrients to the nerve & hence its damage.
Advanced glycation products : When there is high blood sugar due to uncontrolled diabetes, certain by-products known as advanced glycation products are formed. These go and bind to the peripheral nerves preventing their proper functioning.
Inflammatory process : Due to direct result of high blood sugar, certain by-products are formed known as inflammatory markers. These markers cause slow & progressive nerve damage.
The above 3 are some of the main reasons for diabetes to cause neuropathy. This is why the control of blood sugar is the single biggest factor in improving peripheral neuropathy.
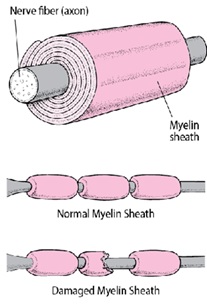
As shown in the previous image, each peripheral nerve fibre is covered by a protective sheath known as myelin sheath. This Myelin sheath completely cover the nerve fibre and protects it from external conditions and diseases.
When this myelin sheath is torn (as shown in the previous pic),the underlying nerve gets damaged & this is known as Peripheral neuropathy.
Why does the myelin sheath gets torn or damaged ?
The myelin sheath gets damaged & causes peripheral neuropathy due to a number of causes. Most common are –
1.Diabetes Mellitus. 2.Hypertension. 3.Vitamin B12 deficiency. 4.Hypothyroidism 5.Older age.
Diabetes Mellitus – This is the commonest cause of peripheral neuropathy in the world. Maintaining a proper blood sugar & HbA1c level will help greatly in improving neuropathy. Unless this is not corrected, no medicine will help the neuropathy.
Vitamin B12 deficiency – This is another common cause of peripheral neuropathy, especially in pure vegetarians (due to lack of B12 in vegetarian diet) & in older people (due to lack of re-absorption or malabsorption of B12 in their gut). Vitamin B12 is largely required for the proper formation of myelin sheath that surrounds the nerves.
Hypothyroidism & Hypertension – Persistent hypothyroidism & hypertension can also cause myelin sheath damage in the long term leading to peripheral neuropathy.
Older age – This is another contributory factor, as with time & age, wear and tear occurs in most people & this leads to nerve damage too.
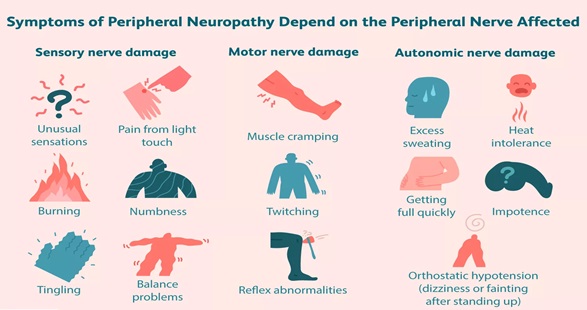
What are the signs & symptoms of peripheral neuropathy ?
Peripheral neuropathy can cause multiple symptoms based on whichever nerve is affected. Some common issues are –
Numbness – It usually starts as numbness followed by tingling or burning sensation. This is usually seen more in ends of the limbs ie. hands &/or feet. It is usually more at night or late evenings, or when lying down to sleep. It is usually better when standing or walking. As time passes, the tingling, burning & pain increases & may lead to weakness.
Eventually, if it is not controlled, after few years, muscle wasting (thinning) occurs. This causes the muscles to become more weak. At this point difficulty in walking & gripping objects may be seen. Difficulty in gripping slipper or climbing stairs, getting up from squatting may be seen Peripheral neuropathy cannot be fully cured, but can be significantly improved with medicine & lifestyle changes.
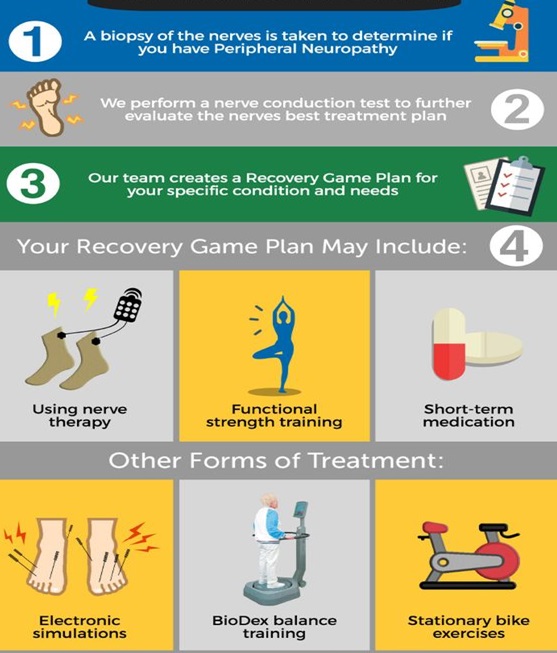
What is the treatment for peripheral neuropathy ?
First, the degree of nerve damage is assessed by doing a nerve conduction study. Then the most likely cause for the neuropathy is identified. (In some cases, this cannot not be identified). After this, a customised treatment depending on the degree of nerve damage & the cause is started. This includes –
- Medications – To improve the symptoms & promote nerve healing.
- Nerve stimulation – In cases of traumatic nerve injuries, brachial plexus injuries or bell’s palsy
- Physiotherapy – To improve the muscle and nerve strength, balance, gait training etc.
- Lifestyle changes – Adequate & in-time food/sleep, regular exercise or walking (especially for those with diabetes, hypertension), proper diet (for those with diabetes, hypertension & vitamin B12 deficiency).