What is Epilepsy ?
Epilepsy is a chronic disorder that causes unprovoked, recurrent seizures. A seizure is a sudden rush of electrical activity in the brain.
What is the difference between seizure and epilepsy?
A Seizure happens when there’s an abnormal electrical discharge in your brain. We all have a 10 percent chance of suffering from a seizure, and that risk increases if you’ve suffered a stroke or brain injury. But a single seizure doesn’t mean you have epilepsy.
Epilepsy is defined as having chronic unprovoked seizures, although anyone can have an episode in their lifetime. Symptoms can vary, including temporary confusion, loss of consciousness or awareness, motor symptoms etc.
What are the causes for Epilepsy ?
In general, there are only 2 causes for epilepsy –
A.Structural change in the brain –brain injury or ischemia. This leads to a structural damage in the brain and this can later lead to seizures. The causes for this have been mentioned above.
B.Functional change in the brain –There is a constant electrical circuit working in the brain. If the child has a minor or major genetic abnormality, this electrical circuit goes out of order and this can lead to seizures. This genetic abnormality can be familial or spontaneously formed (a new mutation & unrelated to the family). There are more than 1000 genetic mutations that can cause epilepsy.
What are the risk factors for Epilepsy ?
- Age – The onset of epilepsy is most common in children and older adults, but the condition can occur at any age.
- Family history of epilepsy
- Head injuries.
- Hypoxic ischemic encephalopathy (birth asphyxia / injury)
- Developmental delay
- Autism spectrum disorder & other neuro-developmental disorders.
- Stroke and other neuro-vascular diseases.
- Dementia & other neuro-degenerative disorders.
- Brain infections.
- Brain tumors.
- Cerebral palsy
- Conditions with intellectual and developmental disabilities
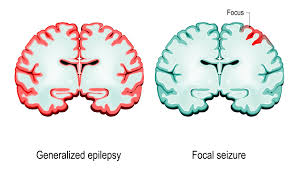
What are the different types of seizures ?
There are many types of seizures, but for practical purposes, they are divided into 2 types –
1.Generalized seizures– They originate from &affect both sides of the brain. Some examples –
● Absence seizures– seen commonly in children between 3-8 years. As the name suggests, children with this seizure temporarily pause, go blank / have an absent stare with or without rapid eye blinking & no response for few seconds followed by complete recovery.
● Tonic-clonic seizures – This may be seen at any age. Typically, the person cries out, loses consciousness, followed by uprolling of eyes and jerky movements of the arms and legs for few minutes usually. Complete recovery is a little slower and more gradual.
2. Focal seizures– Theseare seizures that originate from one area of the brain. Some types are –
● Simple focal seizures affect a small part of the brain (left or right side). They cause small motor movements (like facial twitching or limb jerking) on the opposite side muscles.
● Complex focal seizures can make a person with epilepsy confusedor dazed with or without being able to respond……just like in absence epilepsy.The duration in this however is longer and can affect all age groups.
● Focal with secondary generalized seizures – begin in one part of the brain, butthen spread to both sides of the brain. In other words, the person first has a focal seizure, followed by a generalized seizure.
What is the treatment for Epilepsy ?
Treatment can help most people with epilepsy have fewer seizures, or stop having seizures completely.
Treatments include:
- Medications – medicines called anti-epileptic drugs (AEDs)
- Surgery – to remove a small part of the brain that’s causing the seizures
- Vagal nerve stimulation– a procedure to put a small electrical device inside the body that can help control seizures
- Ketogenic Diet– a special diet (ketogenic diet) that can help control seizures
Medications are the first line of treatment for epilepsy. They do not cure epilepsy but help in stopping the seizures. Eventually, approximately 70% of people with epilepsy can be cured by stopping the seizures for a long period of time.Some people need treatment for life. And some people need a combination of the above treatments for achieving better or complete seizure control.
What is unique about epilepsy treatment at Parijma ?
A.30 years of experience – Specific types of epilepsy require specific types of drugs for faster and better seizure control. With this vast experience of 30 years, the doctors at Parijma are better equipped in prescribing the right drug at the right time.
B.Customised treatment plan – Each person with epilepsy is different and so, a single uniform treatment approach does not work for all. We, at Parijma, after a detailed examination & investigation, prescribe a custom designed treatment plan for each patient.
C.Cutting edge equipment – We, at Parijma, have all the appropriate equipment needed for correctly diagnosing & pin pointing the seizure origin and spread so that the correct diagnosis and drug can be applied.
D.Patient education & awareness – At Parijma, we do not believe in just diagnosing & prescribing medications. We take the time & effort to educate & counsel the patient and family regarding the disorder, the treatment plan, prognosis, “do’s & don’t’s”, effects of the disease & drugs on adolescents, conception (when needed) etc. on a number of occasions. We look at the patient & family as a whole and not just at the disease.